Arduino 25V Voltage Sensor Module User Manual
The Basics
The Arduino analog input is limited to a 5 VDC input. If you wish to measure higher voltages, you will need to resort to another means. One way is to use a voltage divider. The one discussed here is found all over Amazon and eBay.
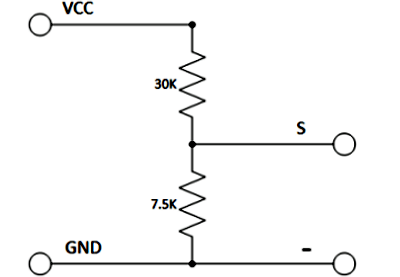
It is fundamentally a 5:1 voltage divider using a 30K and a 7.5K Ohm resistor.
Keep in mind, you are restricted to voltages that are less than 25 volts. More than that and you will exceed the voltage limit of your Arduino input.
Basic Connection
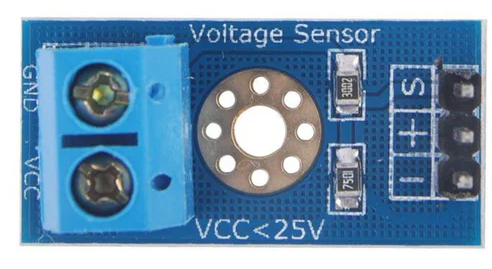
Inputs
- GND – This is where you connect the low side of the voltage you are measuring. Caution! : This is the same electrical point as your Arduino ground.
- VCC: The is where you connect the high side of the voltage you are measuring
Outputs
- S: This connects to your Arduino analog input.
- – (or minus): This connects to your Arduino ground.
- +: This is not connected. It does absolutely nothing… zilch… nada… jack diddly doo doo.
Schematic
The schematic for this is pretty straight forward. As previously mentioned, its just a couple of resistors. In fact, you could build your own in a pinch.
Tutorial
The Connections
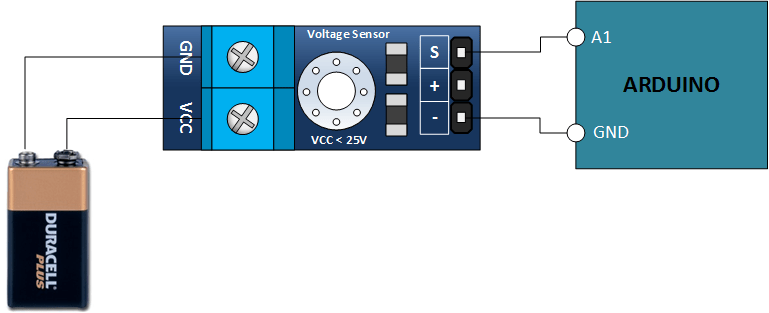
Find yourself a 9 volt battery and connect it, your voltage sensor module and Arduino as shown below.
The Sketch
Enter the following sketch, upload it and go to town. If you open your Arduino serial monitor you will be able to see the voltage.
/*
DC Voltmeter Using a Voltage Divider
Based on Code Created By T.K.Hareendran
*/
int analogInput = A1; // Using A1 as specified in the connection diagram
float vout = 0.0;
float vin = 0.0;
// Using the stated resistor values
float R1 = 30000.0; // Resistance of R1
float R2 = 7500.0; // Resistance of R2
int value = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(analogInput, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("DC VOLTMETER");
}
void loop() {
// read the value at analog input
value = analogRead(analogInput);
vout = (value * 5.0) / 1024.0; // Convert ADC value to voltage at Arduino pin (using 1024 steps)
vin = vout / (R2 / (R1 + R2)); // Calculate the input voltage using the divider ratio
Serial.print("INPUT V= ");
Serial.println(vin, 2); // Print the calculated input voltage with 2 decimal places
delay(500);
}